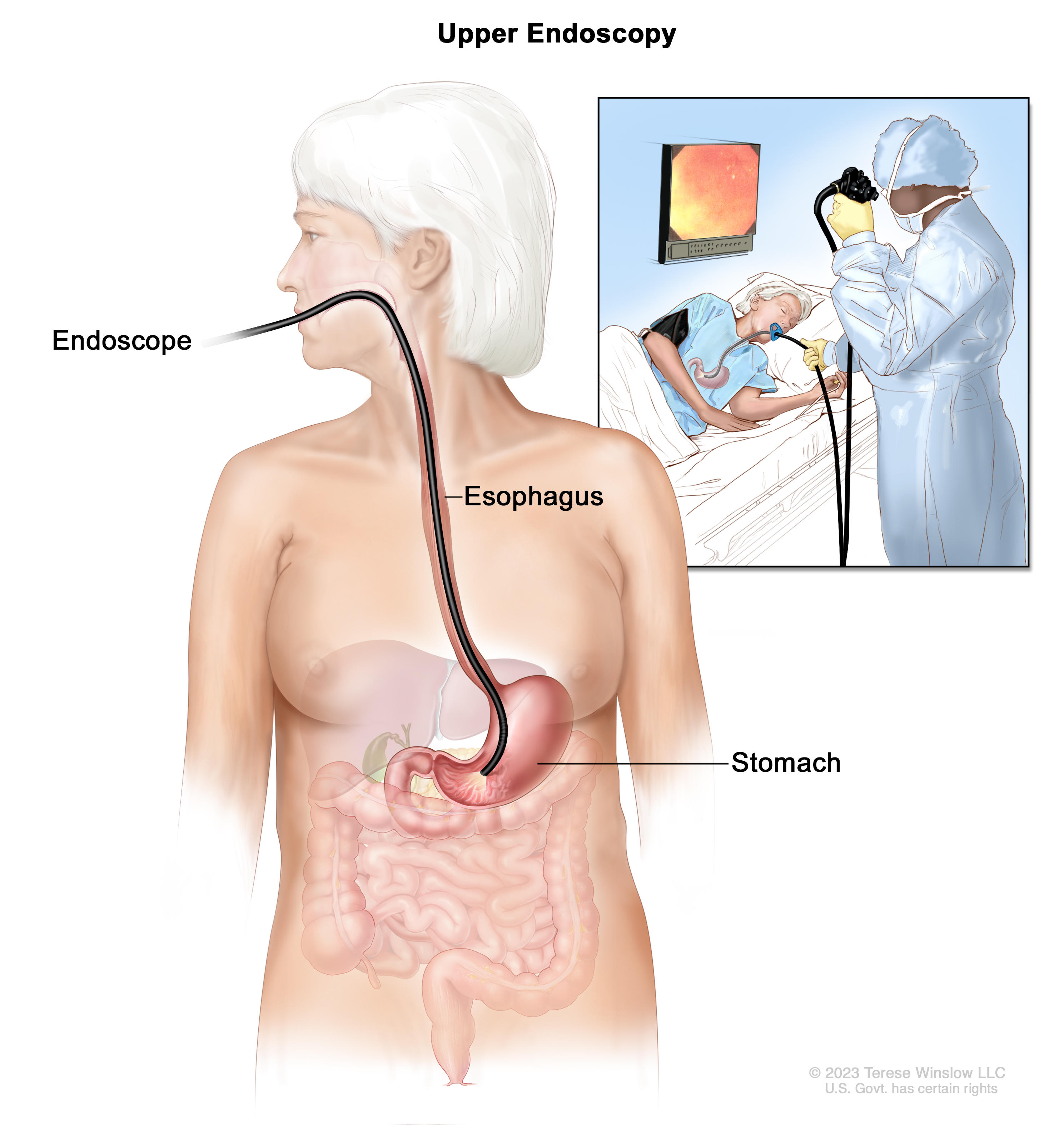
Why Do Young People Get Stomach Cancer?
Experts from the Gastrointestinal Surgery Department at Guangzhou Royal Lee Cancer Center explain: with active treatment, the 5-year survival rate for early-stage stomach cancer can exceed 90%. However, in China, only about 10% of stomach cancer patients are diagnosed in the early stage, with nearly 90% diagnosed in the advanced or even late stage, resulting in a low survival rate.
Therefore, whether to reduce the economic burden or to consider reducing pain and extending life, regular health check-ups are essential.
After all, no matter how advanced the treatment methods for cancer are, they cannot surpass the benefits of timely detection and intervention.
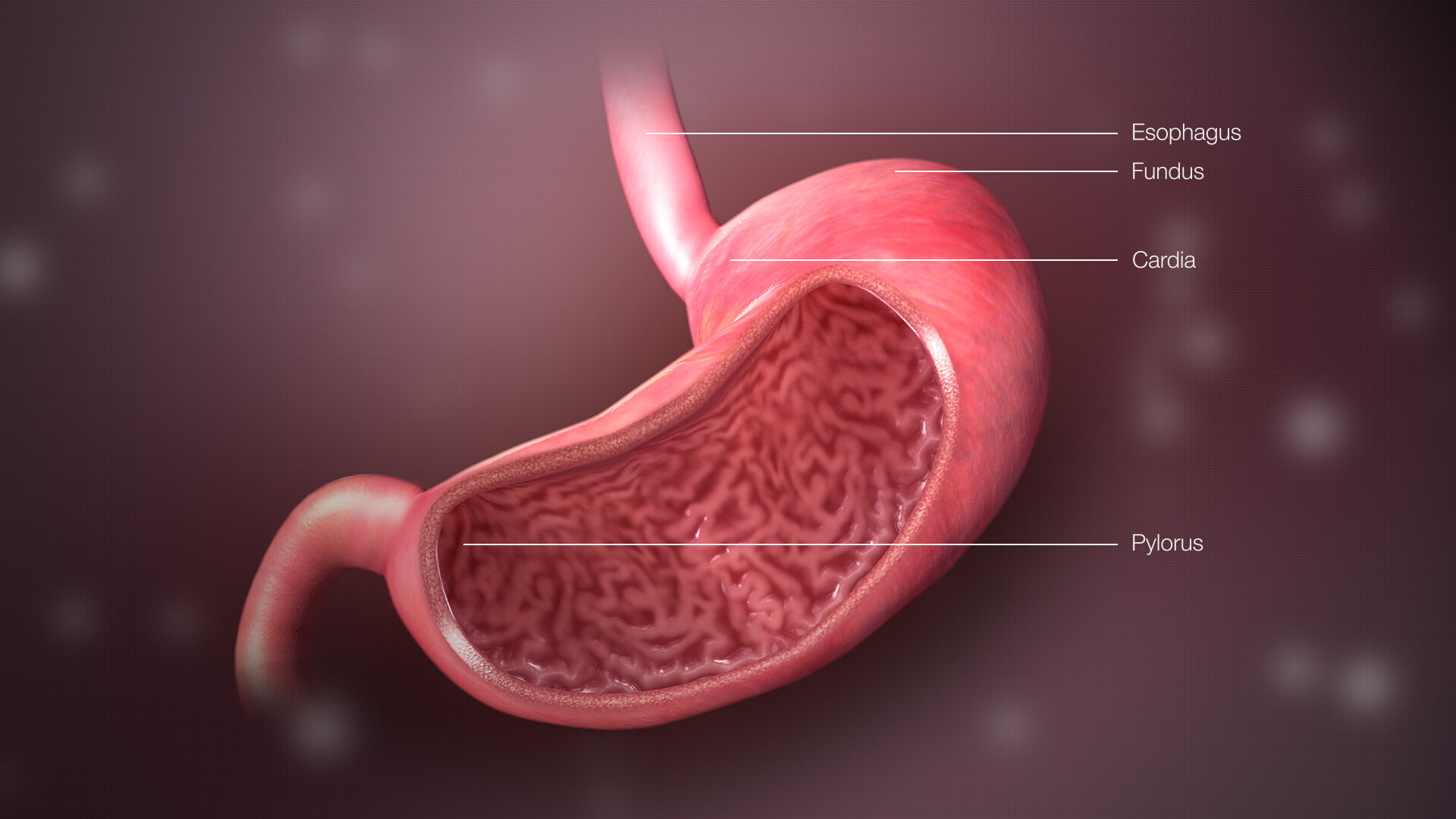

Why are young people prone to stomach cancer?
Stomach cancer is closely linked to lifestyle. Prolonged exposure to high-stress environments, coupled with unhealthy eating habits and long-term staying up late, are the "culprits" that trigger stomach cancer.
These young stomach cancer patients, what have they been doing? Tracing their lifestyles and awareness of disease prevention, it is not difficult to find common issues:
1. Unhealthy eating habits
An imbalanced diet structure, prolonged intake of high-salt foods such as preserved meat, salted fish, and take-out, leads to damage to the gastric mucosa, causing inflammatory irritation, and eventually leading to cancer.
Irregular meals, frequent late-night snacks – young people living this way, if they often experience bloating, acid reflux, indigestion, loss of appetite, etc., should be cautious, as these may be signals of stomach cancer.
2. Neglecting health check-ups, enduring illness
The symptoms of early-stage stomach cancer are very subtle and can easily be overlooked. For example, many young people do not take stomach pain seriously, thinking that enduring it or casually taking a few pills will solve the problem.
3. Suppressing anxiety, negative emotions
Bad moods are also cancer-inducing factors! Psychological factors play an important role in the development of tumors, and people who often experience suppressed emotions and excessive anxiety are more prone to cancer.
Research shows that stomach cancer, liver cancer, and even intracranial malignant tumors are related to irritability, jealousy, and excessive emotional suppression. Maintaining a positive mindset and learning emotional release are also good ways to prevent cancer.
4. Staying up late, overworking the body
Staying up late prevents the stomach from getting necessary rest, weakening the gastric mucosa's self-repair and protection capabilities. As a result, the stomach's resistance decreases, making it difficult to recover when faced with stimuli and damage. When mental stress is too high and the body is overly fatigued, the incidence of stomach diseases also significantly increases.
5. Helicobacter pylori infection
According to surveys, the infection rate of Helicobacter pylori in China is 59%, and Helicobacter pylori is directly related to stomach diseases.
The International Agency for Research on Cancer has classified Helicobacter pylori as a Class I carcinogen for stomach cancer. Abundant research evidence shows that the occurrence of intestinal-type stomach cancer (the majority of stomach cancers) is the result of the combined effects of Helicobacter pylori infection, environmental factors, and genetic factors.
Who needs screening?
In China, the defined target population for stomach cancer screening is aged ≥40 years and meets any of the following criteria, suggesting that they should be screened for stomach cancer:
① Population in high-incidence areas of stomach cancer;
② HP infected individuals;
③ Individuals with a history of chronic atrophic gastritis, gastric ulcers, gastric polyps, residual stomach after surgery, hypertrophic gastritis, malignant anemia, and other precancerous diseases;
④ First-degree relatives of stomach cancer patients;
⑤ Individuals with other risk factors for stomach cancer (such as high-salt intake, pickled diets, smoking, heavy alcohol consumption, etc.).