SPECT/CT integrates high-end ECT and spiral CT into a large-scale device. In addition to providing the organ tissue functional information reflected by ECT, it also offers the anatomical information of CT. Through the fusion imaging technology, functional images are overlaid with anatomical images, further enhancing the accuracy of disease diagnosis.
To further improve medical quality and provide more powerful support for the diagnosis and treatment of clinical diseases, the Nuclear Medicine Department of Guangzhou Royal Lee Cancer Center has introduced a GE NM/CT 860 SPECT/CT from the United States.
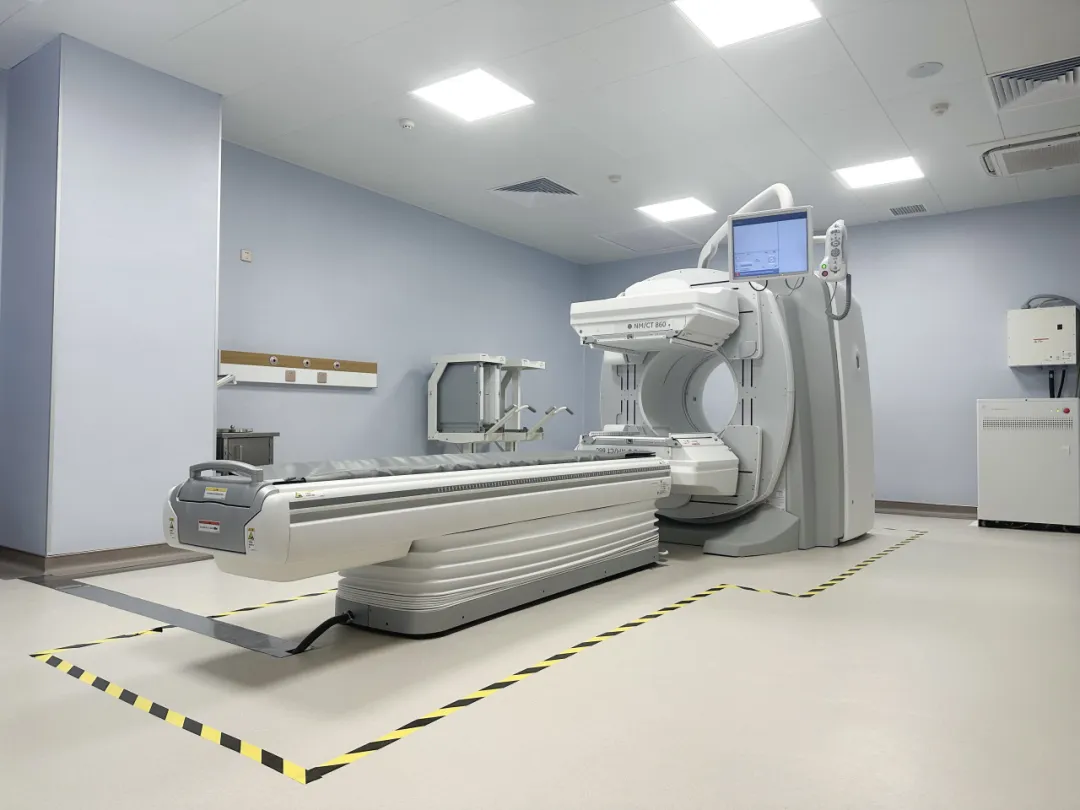

This equipment is currently one of the more advanced integrated nuclear medicine diagnostic instruments in China, equipped with three core innovative technologies unique to GE: Smart Dual Energy Selector, spiral-like acquisition mode, and HD core noise reduction technology. By reducing noise at the source of signal acquisition and improving the sensitivity and image resolution of SPECT/CT imaging, it shortens scanning time, improves examination efficiency, and provides assistance for more precise and efficient nuclear medicine imaging diagnosis.
This new equipment not only demonstrates unique advantages in functional diagnosis, early diagnosis, and treatment efficacy verification of thyroid diseases, tumor bone metastasis, urinary system, circulatory system, digestive system, and other diseases, but also plays an important role in clinical research.
The introduction of SPECT/CT technology in our hospital will undoubtedly assist in the improvement of the diagnosis and treatment level of nuclear medicine; at the same time, it will provide more accurate and comprehensive reference data for clinical diagnosis, help enhance the comprehensive diagnosis and treatment level of Guangzhou Royal Lee Cancer Center, and bring better medical services to the vast number of patients.
Main Clinical Applications of SPECT/CT in Nuclear Medicine Department:
1. Thyroid Imaging
Used for the diagnosis and localization of ectopic thyroid; assessment of thyroid nodule function and differentiation of benign and malignant nodules; localization and diagnosis of metastases from well-differentiated thyroid cancer; estimation of thyroid size and weight, guiding iodine-131 treatment for hyperthyroidism.
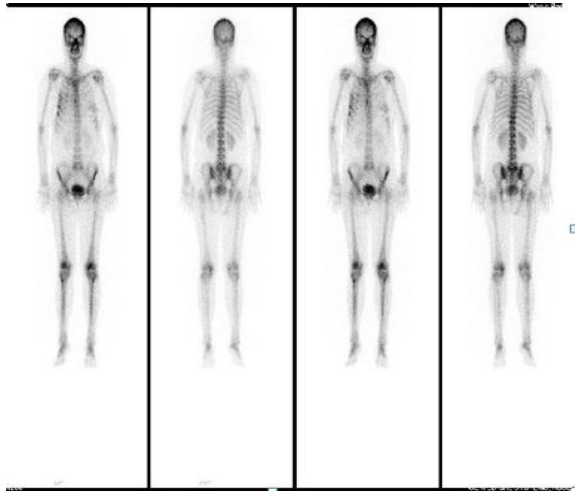
2. Whole-body Bone Imaging
It is the preferred method for early diagnosis of malignant tumor bone metastasis. It can be used for disease staging, evaluation of bone pain, prognosis assessment, efficacy observation, and detection of high-risk sites for pathological fractures. SPECT/CT fusion imaging greatly improves diagnostic sensitivity, specificity, and localization accuracy.
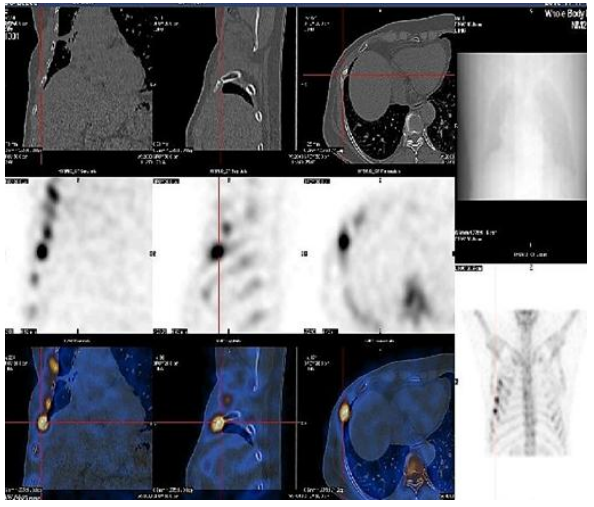


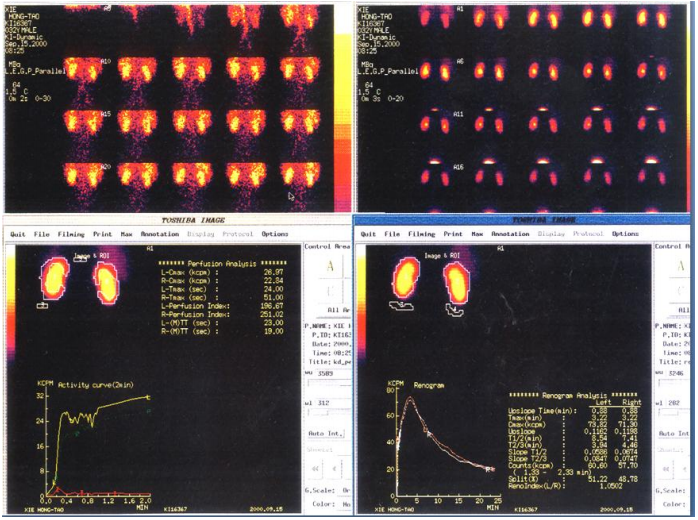
3. Renal Imaging
Understanding renal arterial lesions and bilateral renal blood supply; assessment of renal function and split renal function, especially important in monitoring renal function during chemotherapy for malignant tumors. Understanding the patency of the upper urinary tract and diagnosing urinary tract obstruction; non-invasive diagnosis and monitoring of bladder ureteral reflux; understanding the impact of diabetes on renal function.
4. Parathyroid Imaging
Diagnosis and precise localization of parathyroid adenomas (including ectopic ones).
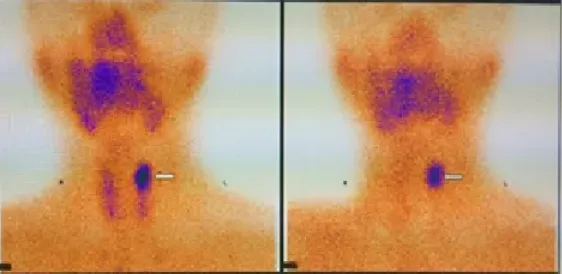

5. Salivary Gland Imaging
Used for the assessment of salivary gland function, such as the diagnosis of dry syndrome, residual gland or transplanted gland function after salivary gland surgery, and the diagnosis of occupying lesions, such as lymphoepithelial cysts.
6. Iodine 131 Whole-body Imaging
It is one of the most important methods for pre-treatment evaluation, metastatic lesion diagnosis, efficacy assessment, and dynamic evaluation before differentiated thyroid cancer iodine-131 treatment. SPECT/CT fusion imaging greatly improves diagnostic sensitivity and specificity.
7. Pulmonary Perfusion Imaging
Non-invasively displays the distribution of pulmonary blood flow, which plays an important role in diagnosing pulmonary artery embolism when combined with pulmonary ventilation imaging; it is also the necessary and only means for determining hepatic hemodynamic shunt measurement before selective internal radiation therapy (SIRT) for liver tumors (primary liver cancer, metastatic tumors).
